If you’re a woman, you’ve probably heard that women are at risk for coronary heart disease, but you may be wondering what is this? Then read on to learn about its symptoms, treatment options, and risk factors. You’ll be surprised at how easy it can be to prevent this condition.
Atherosclerosis
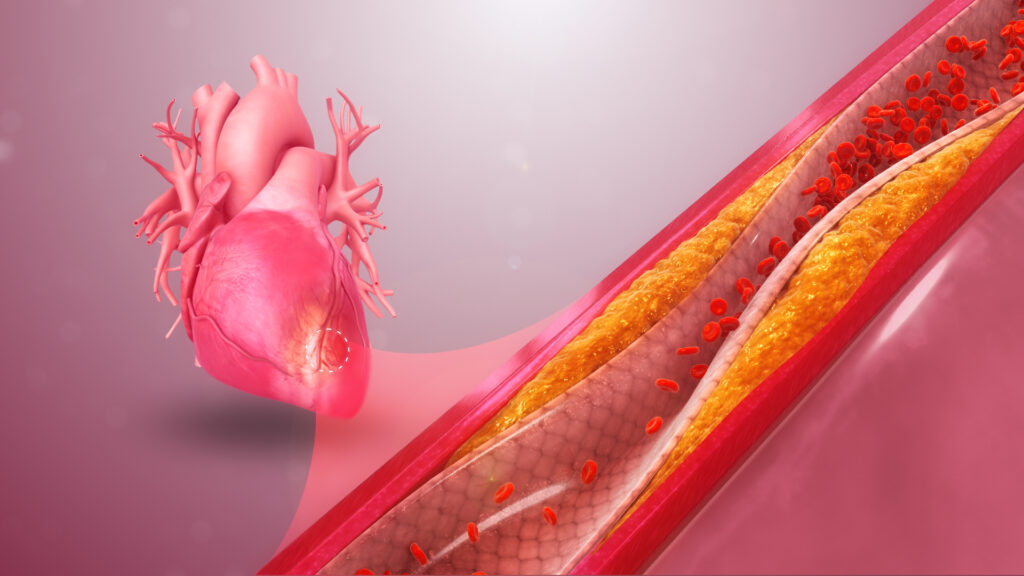
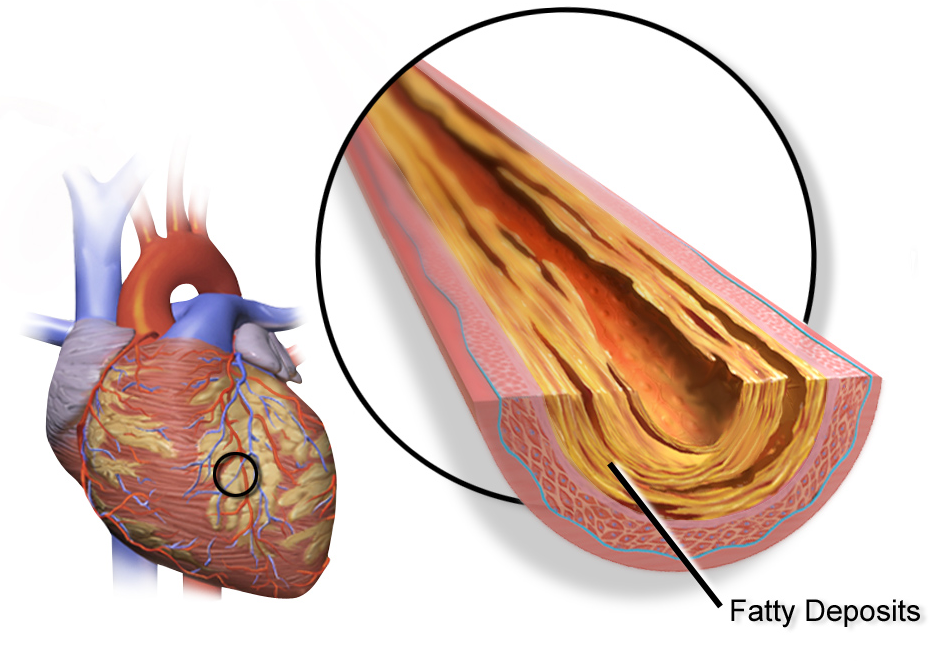
Atherosclerosis is a condition where the arteries that transport blood from the heart to the rest of the body become thick and clogged with plaque. This causes reduced blood flow and reduces the amount of oxygen that is supplied to the organs. When this happens, it can cause life threatening problems. Fortunately, there are some ways you can prevent and treat atherosclerosis.
The best way to avoid atherosclerosis is to lead a healthy lifestyle. You can also reduce your risk of atherosclerosis by reducing your blood pressure, eating a healthy diet and exercise.
Those who have atherosclerosis should consult a doctor as soon as they notice any symptoms. Early treatment can help prevent a heart attack or stroke. These symptoms may include shortness of breath, fatigue, muscle weakness, numbness, and chest pain.
Obesity
Obesity is a global epidemic. It is a major cause of excess morbidity in women and in the United States. It also contributes to cardiovascular disease (CVD), diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and sleep disorders. In addition, obesity increases the risk of cardiovascular mortality.
In recent years, studies have investigated whether or not obesity is a primary contributor to coronary heart disease. In particular, we investigated whether obesity is a risk factor for STEMI in young patients.
Our results show that obesity is a significant comorbidity in STEMI patients. Overweight was present in 78 percent of the cohort. However, obesity did not correlate with greater overall survival or a lower rate of recurrent STEMI.
The relative magnitude of the effect of obesity on the incidence of coronary heart disease is likely to be much greater than the results suggest. Although we did not find an association between adiposity and nonfatal myocardial infarction, we did find an association between adiposity, metabolic syndrome, and cardiorespiratory fitness.
Lack of exercise
Lack of exercise is one of the leading risk factors for coronary heart disease. Studies have shown that regular physical activity can help you maintain a healthy weight, prevent diabetes and cardiovascular disease, and even reduce your risk of cancer.
In the United States, there is a high prevalence of sedentary behavior, which can increase the risk of obesity, diabetes, high blood pressure, and coronary heart disease. Physical inactivity is a factor in many of the noncommunicable diseases that kill more than 750,000 people each year.
While the health benefits of regular physical activity are well documented, the optimal amount of exercise to get is still unclear. Researchers recommend getting at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity activity at least five times per week. However, you should speak with your doctor about the intensity of your workout before you begin.
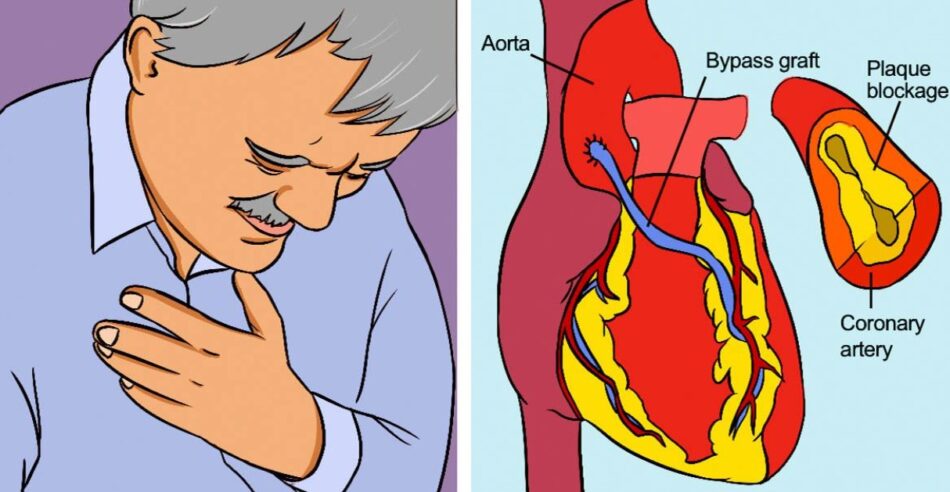
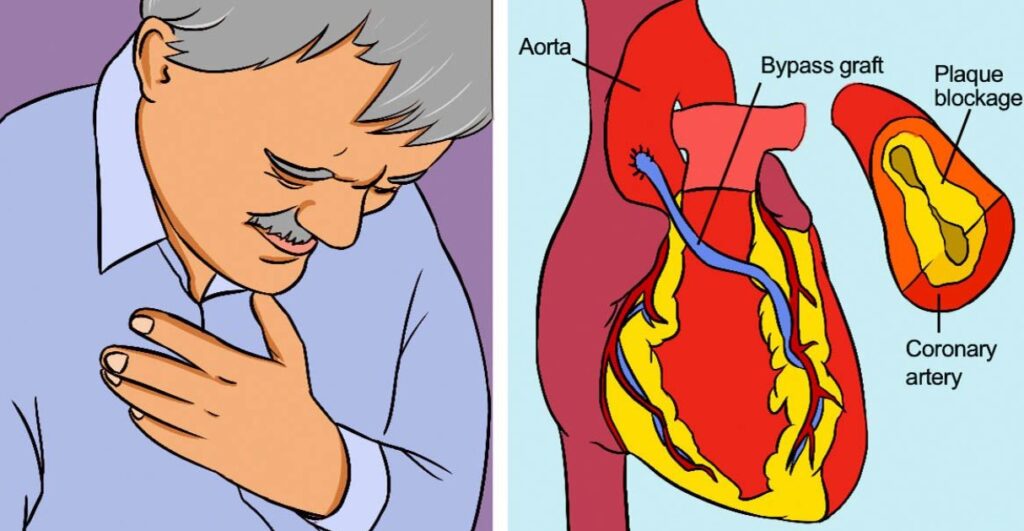
Cardiovascular bypass surgery
Cardiovascular bypass surgery is a procedure that involves removing plaque from blocked coronary arteries. This reduces the risk of blood clots, which can lead to serious heart attacks. It also provides a better flow of blood to the heart.
The procedure varies depending on the artery that is blocked. In some cases, the procedure will be minimally invasive.
A cardiothoracic surgeon will create an incision in the center of the chest. Next, the surgeon will lift the rib cage and spread the bones. Afterward, a sterile dressing will be applied. After the bone heals, a wire will be inserted.
During the surgery, the anesthesiologist will keep an eye on the patient’s vital signs. A special cleansing solution will be used on the skin.
The procedure is often performed under general anesthesia. Some patients may require a breathing tube. These tubes will be attached to a ventilator. Once the patient can breathe on his or her own, these tubes will be removed.
Symptoms
Coronary heart disease, also known as CAD, occurs when fatty deposits (plaque) build up in the walls of arteries that supply blood to the heart. These deposits cause narrowing of the arteries, making it difficult for oxygen-rich blood to reach the heart.
Some people with CAD don’t experience symptoms for a long time. Eventually, plaque ruptures and causes a blockage. This is a medical emergency and can lead to a heart attack.
A heart attack is the most serious complication of coronary artery disease. It can be fatal if not treated quickly. If you think you might have a heart attack, call triple zero and go to the nearest hospital.
When you have a heart attack, you may feel a heaviness or pressure in your chest. You may also feel shortness of breath or indigestion.